Why it’s not just the marketing department that should be interested in market research
Monday, March 30, 2020
Market research is the systematic collection and evaluation of market data (e.g., from customers and the competition) with the aim of making the right decisions with regard to the development and modification of devices, marketing actions and much more.
Market research helps companies:
- Discover market opportunities
- Avoid risks and bad decisions
- Meet regulatory requirements
Use appropriate market research methods precisely during the device lifecycleMarket research will be successful if companies:
- Don’t see market research as just the job of the marketing department
In the article below, we give you answers to the six most frequently asked questions and give you four tips for saving time and money during market research.
A) Intended targets: who should be interested in market research
Market research is a tool for answering important questions regarding the different functions of a company:
- DEV: Development (including usability engineering)
- DM: Device management (including requirements engineering and marketing)
- RA: Regulatory affairs
- CA: Clinical affairs
- M: Management
1. Product-related questions
A lot of questions relate to the devices and services:
Question | DEV | DM | RA | CA | M |
How do our customers work with our devices and services? | X | X | X | ||
What do they appreciate, what do they not like? | X | ||||
What problems occur? | X | X | X | X | X |
How do our devices and services compare to the competition? | X | X | X | ||
What would we have to change in the existing devices and services in order to increase the benefits and customer satisfaction? | X | X | X | ||
Which devices and services do my customers need that we do not offer? | X | X | |||
How should we design our devices? | X | X | |||
Which devices and services should we no longer offer? | X | ||||
What risks associated with our device? | X | X | X | X | X |
2. Marketing issues
Other questions relate to additional marketing aspects:
Question | DEV | DM | RA | CA | M |
What price can we charge for our devices and services? | X | X | |||
What do our customers see as the alternatives to our devices and services? | X | X | X | ||
Who are the participants in our markets? | X | X | |||
Which are the best channels for us to use to communicate with our customers? | X | ||||
Which are the best channels for offering our devices and services? | X | ||||
How effective are our marketing actions? | X | ||||
What market shares and sales can we achieve? | X | X |
3. General questions
Market research can also provide important information for company management.
Question | DEV | DM | RA | CA | M |
What should our priorities be and what order should actions be taken in (e.g., with regard to devices and marketing)? | X | X | X | X | X |
What are the risks for our company? | X |
B) How market research should be carried out
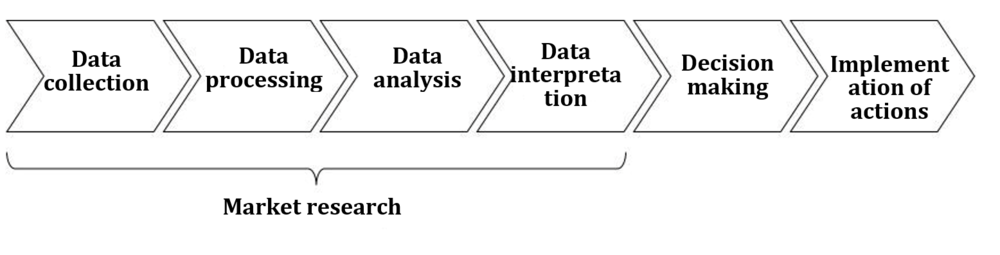
Market research is defined (see, for example, Marketingmanagement by Christian Homburg (2017), page 250) as “the systematic collection, processing, analysis and interpretation of data on markets (customers and competitors) for the purpose of underpinning marketing decisions.” Market research answers questions, but does not make decisions or implement actions (see Fig. 1).
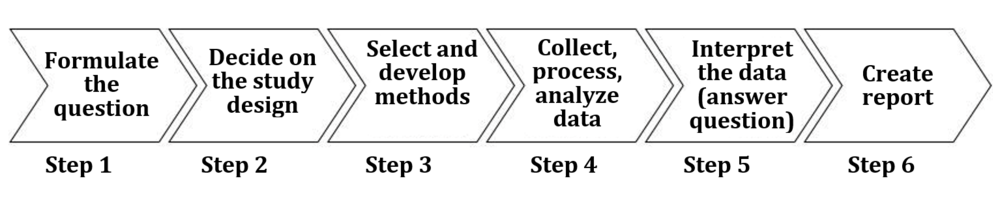
Step 1: formulating the question, defining the problem
Formulating the question precisely is crucial for the success of market research. We often talk about the decision problem to be solved. From this decision problem, we can usually to derive one or more research problems that are even more specific than the original decision problem.
Decision problem | Research problem |
What device should we develop? | What are the requirements of the potential stakeholders? |
How should the new device be designed? | Which of several design proposals is the best? |
How can we improve an existing device? | What are the usability problems? How do our customers compare our device with the competing devices? |
Step 2: deciding on the study design
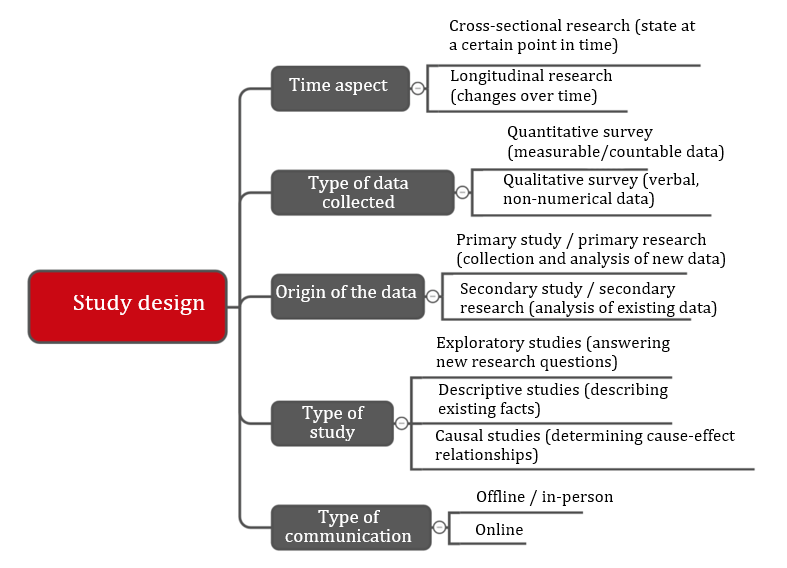
The study design should be based on the question being asked. Different criteria can be used to classify studies (see Fig. 3).
Time aspect
Cross-sectional research involves methods to collect and analyze information at a given point in time.
In contrast, the aim of longitudinal research is to observe changes over a period of time. In longitudinal research, the same methods are often used several times, e.g., surveys are conducted several times.
Quantitative and qualitative data collection
Studies often combine quantitative and qualitative data collection methods. Examples of quantitative methods are:
- Online questionnaires with a Likert Scale
- Measuring use errors and the time needed to complete tasks in usability tests
Qualitative methods include interviews and context analysis.
Primary research versus secondary research
Another difference is whether the objective of the research can be achieved by analyzing previously collected data (secondary research) or not. If this is not possible, new data will have to be collected (primary research).
The methods mentioned above are used to collect new data, i.e., primary research.
Exploratory, descriptive and causal studies
Lastly, studies can be classified by type:
Type of question | Type of study | Example |
Answering new research questions | Exploratory studies | What are the stakeholder requirements of nursing staff for documenting drug complications? |
Description of existing facts | Descriptive studies | How do nursing staff currently document drug complications? |
Determination of cause-effect relationships | Causal studies | How does the training of nursing staff affect the correct documentation of drug complications? |
Type of communication
In addition to face-to-face meetings (observation, surveys), online-based market research has become more important. Examples are:
- Online surveys: The classic “survey” with questionnaires can be evaluated quickly. However, validation is more complex and its scope of application is limited.
- Online and webcam interviews: A moderator and one or more participants can also meet online on a real-time platform. In 1:1 communication, respondents are asked to explain what or how they think, for example, regarding an aspect of a device. Moderators also learn about the perspectives, motives and experiences of the participants, as well as the language they use. These platforms are also suitable for 1:n communication, e.g., for focus groups.
- Online focus groups:
- Chat-based: This option is useful when simplicity and immediacy are high priorities. The technical requirements are relatively low. 90 minutes or even less is usually enough.
- Webcam-based: Real-time platforms on which the moderator and participants can meet online. Sessions often last between 1.5 and 2 hours, and the moderators can see and hear what the participants are saying.
- Remote usability tests, in which participants work with devices at home or their place of work and are observed and asked questions by a remote test leader. Remote usability tests can be divided into two categories:
- Moderated: Allows interaction between participant and moderator as both are online at the same time. The moderators can ask questions for clarifications or delve deeper into the topic by asking additional questions after the task has been completed.
- Unmoderated: Tests are carried out by the participant alone. Even though there is no real-time interaction with the participant, some tools for remote studies allow you to incorporate follow-up questions into the study that can be shown after each task or at the end of the session.
Step 3 selecting and developing methods
The method must fit the question
The methods must be suitable for answering the specific questions being asked, particularly the research problem.
Research problem | Potential methods |
What are the requirements of the potential stakeholders? | Context analyses, surveys |
Which of several design proposals is the best? | A/B tests, benchmark tests |
What are the usability problems? How do our customers compare our device with the competing devices? | Participant and non-participant observation |
Examples of methods
Market research uses such a wide variety of methods that they cannot all be named here. The following methods have been successfully used at the Johner Institute for projects with medical device manufacturers:
- Context analyses
- Group discussions
- In-depth interviews
- Case studies
- Ethnographic market research
- Quantitative online surveys, e.g., with single and multi-item scales
- Qualitative oral surveys, e.g., based on key questions (structured interviews)
- Quantitative and qualitative written surveys with questionnaires
- Participant and non-participant observation (including usability tests)
- A/B tests
- Benchmark tests
Developing methods
Developing the method includes for example:
- Selecting a measuring instrument, such as Likert scales
- Designing and validating questionnaires
- Creating “recruitment screeners”
Step 4: collecting, processing and analyzing data
Data collection: This is the phase that requires the most resources, i.e., staff, time and budget. For the data collection, it is important that the people collecting the data have been trained sufficiently.
Data analysis: For the data analysis, statistical methods are generally used to condense data and draw conclusions from the results. The following techniques are often used for this:
- Descriptive methods such as statistical measures and frequency tables
- Estimates and statistical tests
- Multivariate methods
Step 5: interpreting data, answering questions
The results from step 4 are the “naked results.” Now you have to draw conclusions from these results and answer the initial question. The people in charge should also discuss weaknesses resulting from, e.g., the:
- Type of question
- Choice of study design and methods
- Performance of the study (including data collection, processing and analysis)
Step 6: writing the report
The last step of market research is writing a report that summarizes the main findings and gives recommendations for future action.
From now on, it is up to others to make decisions and implement actions (see Fig. 2).
C) Answers to frequently asked questions about market research
1. How many subjects or respondents do you need for a market research study?
For a simple exploratory study, as few as five respondents can be enough for meaningful results. Quantitative surveys usually require a much higher number.
The number of respondents generally depends on various factors such as the:
- Question, research problem
- Choice of method
- Required level of accuracy
2. How much does a market research study cost?
Companies can obtain important insights even with a four-figure sum. Of course, there are questions that require six and seven-figure outlays.
However, companies should be aware that a higher sample size/cost will usually result in more data, but not necessarily in greater insight.
3. What should be outsourced and what shouldn’t?
The activities that companies should outsource depends on the following parameters:
- Their own level of competence
- Availability of resources (experts, finances)
- Strategic alignment (e.g., is a study going to be repeated regularly?)
- Number of studies
As a rule of thumb, manufacturers should not outsource these activities:
- Development of the question
- Decision making
- Implementation of actions
In contrast, it has been shown to be a good idea to call on outside help for the following, at least initially:
- Planning of the study, selection of the methods
- Recruitment of subjects
- Collection, evaluation and analysis of data
4. Who carries out market research?
In German-speaking countries, there are “all-round market research institutes.” These are companies that carry out research using different methods (surveys, product tests, etc.) on a wide range of products. “All-round” because these companies do not specialize in one sector.
The largest of these companies are:
- GfK-Gruppe
- Kantar TNS
- Nielsen Company
- Ipsos Gruppe
In addition to the above “all-rounders”, there are also specialized institutes that focus on medical devices, among other things - for, example the Johner Institute :-).
5. What should you look out for when outsourcing to third parties?
Select partners that meet these criteria:
- Proven competence in the application of market research methods
- Knowledge of regulatory requirements (including those of the relevant sector)
- Experience with the product class and sector, e.g., to be able to better identify specific problems
- For medical device and pharmaceutical manufacturers, certification e.g., ISO 13485, to avoid audit problems (key point: outsourced processes and supplier management)
6. What are the common typical mistakes?
- Research is often carried out without taking the decision problem into account. This means that the results cannot be used to answer the question.
- The personnel deployed are not sufficiently qualified. The belief that you can do everything yourself and that anyone can do the work has caused numerous studies to fail or to produce misleading results.
- The number of samples chosen is too small, people rely on numbers that are not statistically reliable.
- Even larger samples might not be representative if no attention has been paid to ensuring they are, if what “representative” means wasn’t been defined precisely enough or if it wasn’t possible to recruit representative subjects.
- Correlations are confused with causalities, leading to incorrect conclusions being drawn as a result.
D) Practical tips for successful market research
1. Comply with the law
As boring as it seems: research and comply with the legislation.
Data protection
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and supplementary Federal Data Protection Act (BDSG) are the basic data protection laws.
Collecting data as part of marketing and opinion surveys is only permitted if the survey participants have given their prior effective consent in accordance with Article 6 of the GDPR.
The new Federal Data Protection Act, in contrast to the previous version (§30a), only explicitly addresses market and opinion research at one point:
If they [the controller or processor] commercially process personal data [...] for purposes of market or opinion research, they shall designate a data protection officer regardless of the number of persons employed in processing.
This means that you must always appoint a data protection officer when you conduct market or opinion research.
Unfair competition
The Act against Unfair Competition (UWG) also has to be taken into account. Breaching Section 7 “Unacceptable nuisance” is also a regulatory offense.
Medical device law
For medical device manufacturers, there can be an overlap between market research and activities that are regulated by medical device law, such as:
- Pre-market activities, especially device development e.g.:
- Determining stakeholder requirements
- Formative and summative usability evaluations
- Clinical investigations
- Post-market activities:
- Post-market surveillance
- Post-market clinical follow-up
In these cases, the corresponding legal (MDR, IVDR, MPDG) and standard (e.g., IEC 62366-1, ISO 13485) requirements apply.
2. Pay attention to objectivity
It is particularly difficult to stay objective when it comes to some devices. But a market researcher is there to ensure that the methodology is as unbiased as possible and that the result is as objective as possible, regardless of the question or problem.
There is no point in lying to yourself or choosing a method that will produce the results you want. A neutral expert pays attention to:
- The wording of each question and the order in which the questions are asked in an interview
- The make-up of focus groups and respondent groups
- The interpretation and evaluation of results, e.g., of use errors in usability tests
The aim should always to be to gain new insights and answer the question. You should not misuse market research to confirm preexisting opinions.
3. Use “incentives” to make sure that the subjects appear
The challenges involved in market research are not just about recruiting respondents. It is, in fact, sometimes more difficult to make sure that the respondents actually turn up at the agreed time (e.g., for a usability test or a focus group).
This is where “incentives” come into play. Money seems to be a great incentive. The value of the “incentive” should be set based on the target group and the duration of the meeting.
One unique feature of medical device market research is that a lot of subjects see helping to develop medical devices that help patients as an additional motivation.
If respondents agree to participate in a study, the “incentive” ensures that they come.
4. Avoid group dynamics
Homogeneous focus groups create a “safe space” where people are more likely to express their thoughts and feelings. They stop damaging group dynamics from forming:
- Younger people feel intimidated by more experienced, older people.
- Nurses feel that they cannot speak freely in front of physicians.
For usability tests, particularly for the summative evaluation, it can even be vital that the tests are carried out with the respondents individually. This can prevent the respondents from influencing one another and distorting the results of the study as a result.
E) Unique features for medical device manufacturers
As explained above, market research activities can overlap with regulated activities. Manufacturers should take advantage of this:
- The formative evaluation can be carried out with market research methods. The list of methods in TR IEC 62366-2 has a lot of similarities with the list of methods above.
- Usability tests in the form of a participant observation is used both for market research and for the summative evaluation.
- Market research can be combined perfectly with the post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF). The follow-up of devices that is standard is market research also provides additional data on the performance and safety of the devices.
- The Johner Institute recommends using the context method as per ISO 9241-110 to collect the stakeholder requirements (particularly the “user requirements”). This method is also part of the market research arsenal.
Tip
Medical device manufacturers shouldn’t view market research as just an instrument for device management
and marketing. Instead, market research methods should be used throughout a device's entire life cycle (while the regulatory requirements taking into account at all times).
F) Support from the Johner Institute
The Johner Institute can support medical device manufacturers:
- Formulate their question and define their decision problem
- Plan, perform and analyze market research studies
Typical tasks that manufacturers outsource to the Johner Institut include:
- Device development
- Identifying actual user group(s) and context of use
- Identifying usability and stakeholder requirements
- Carrying out formative and summative evaluations
- Preparing authorization dossiers that comply with the relevant standards and laws
- Market and competitor analyses, benchmarking
Finding out:- which comparable devices are available on the market and what features these devices offer
- which devices features are well or less well-received by users and which features are missing
- how you device compares to one or more competing devices This will help you to quickly find out how you can optimize your device further or even if additional functions need to be developed.
- Post-market activities
- Carrying out the post-market surveillance
- Carrying out the post-market clinical follow-up (PMCF) and updating clinical evaluations
Further Information
Do you want to learn more about market research? Do you want to know how you can avoid unnecessary (regulatory) costs and make your devices even more successful on the market?
Then please contact us.
G) Conclusion and summary
A lot of companies just use market research as a marketing instrument. But all departments in a company - from development to device management through to clinical affairs and management - should make use of market research techniques.
Precisely conducted market research offers many advantages:
- Save time and money
Market research helps manufacturers set priorities correctly, find the best design for their device and avoiding bad developments. - Achieve regulatory compliance
Market research techniques, such as formative and summative evaluations and context analysis, don’t just help save manufacturers money, they also directly help them comply with regulatory requirements. - Manufacture safe devices
Particularly in the case of medical devices, it is not just market success that matters - the safety of the device for patients, users and third parties is also vital. Here too, market research offers an effective arsenal of methods. Market research in the post-market phase helps to promptly identify and improve unsafe products. - Achieve customer satisfaction and market success
The obvious goal of market research is to be successful on the market: with good devices and effective communication. - Avoid business risks
Anyone who doesn’t know their competitors is taking an unnecessary risk. Market research offers a systematic approach to competitor analysis. But it does more than that: It helps manufacturers make safer decisions and avoid bad decisions by providing reliable data.
The variety of methods is like a suitcase full of tools: if you don’t master them, you do more harm than good. People who know how to use them will find it easier to carry out their tasks and benefit from the advantages described above.
Contact us right away if you are interessted in market research for your medical device.
Author: Immanuel Bader